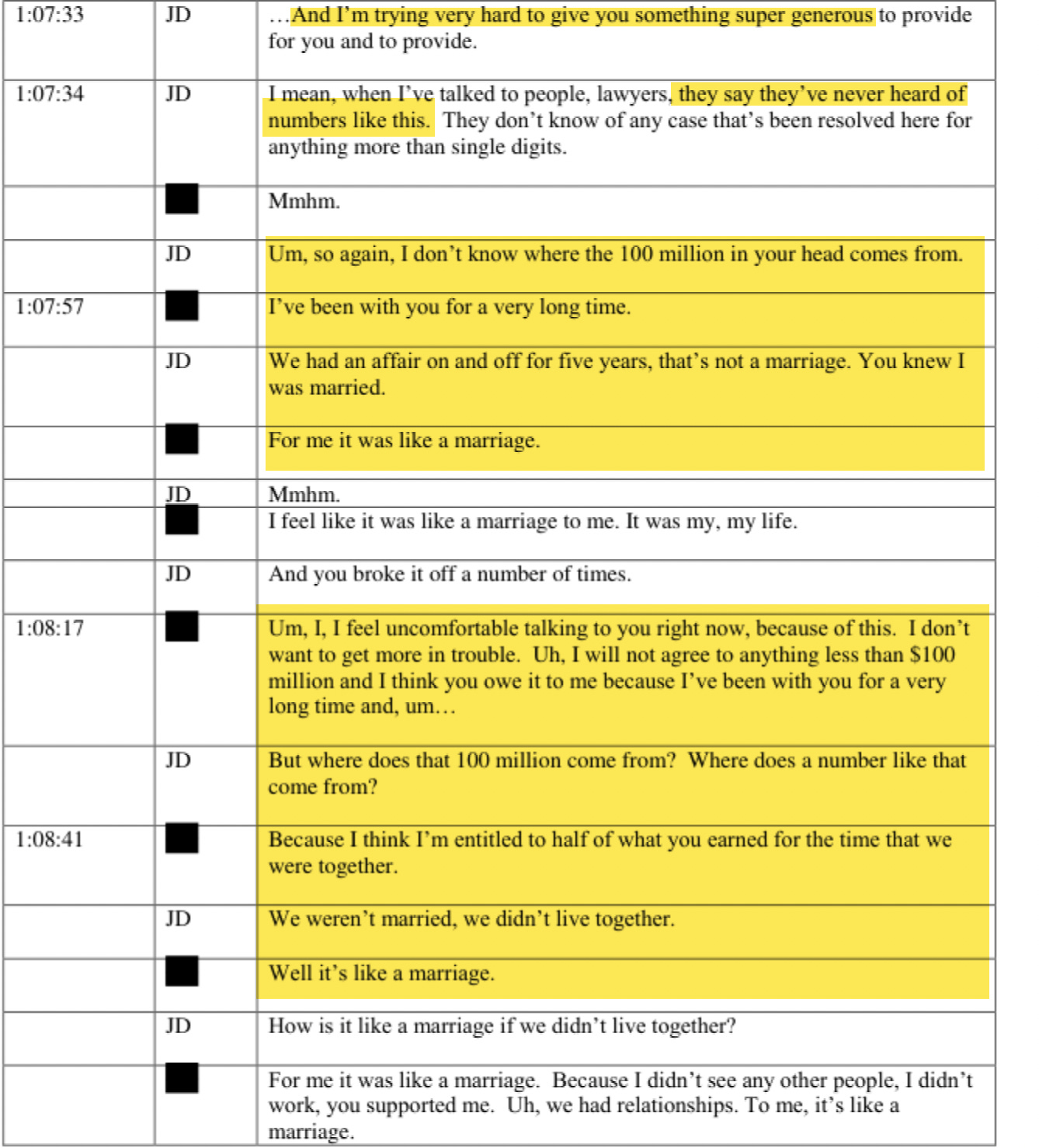
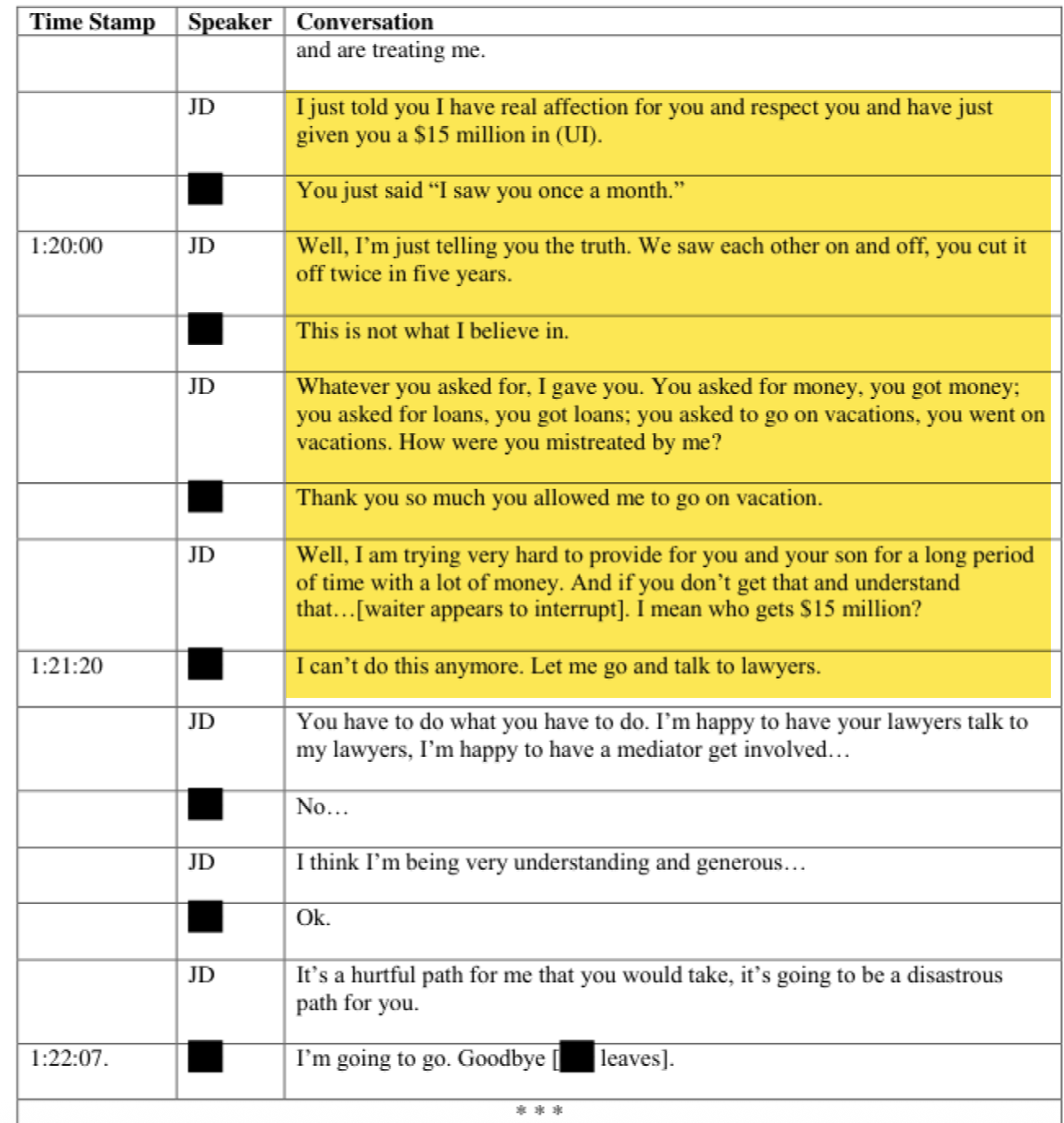
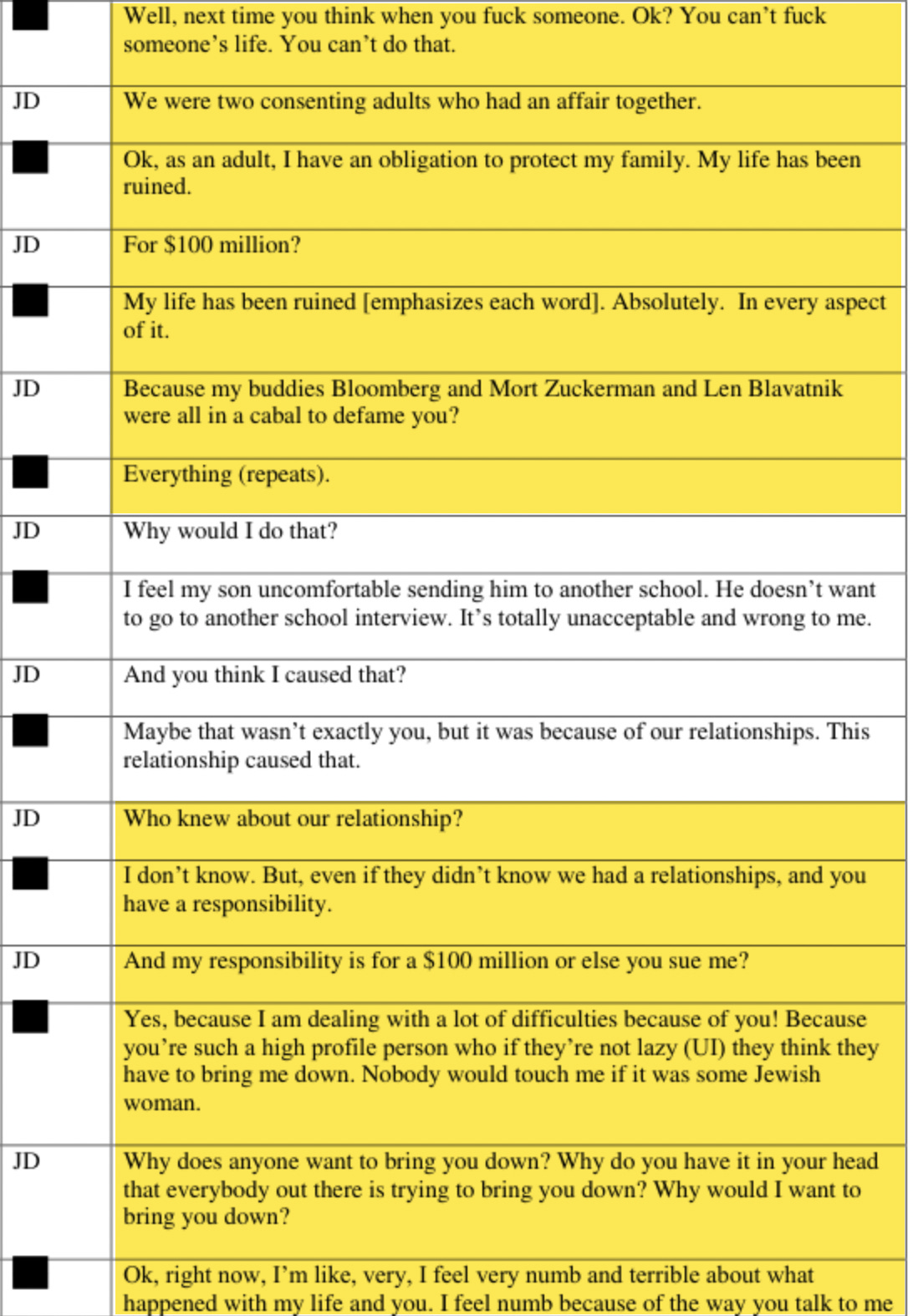
Note: This is the transcript of a recent episode of System Update. Watch the full episode here, exclusively on Rumble: 
Exactly four years ago this week, British law enforcement agents marched into the Ecuadorean Embassy in London and arrested the publisher, journalist and WikiLeaks founder, Julian Assange, the person who has quite possibly published more major scoops than any journalist of his generation. Ever since Assange has been imprisoned in the high-security prison called His Majesty's Prison Belmarsh, a facility so repressive and severe that it has been used for dangerous terror suspects and the BBC, in 2004, called it Britain's Guantanamo Bay. Assange’s imprisonment continues to this very day, despite his never having been convicted of any crime other than a bail-jumping misdemeanor for which he long ago served his government sentence. Instead, he is now being held in that prison solely because the Biden administration is demanding that he be extradited to stand trial in the United States – a country of which he is not a citizen and which he has barely visited – on espionage charges in connection with the 2010 reporting that WikiLeaks did on U.S. war crimes in Iraq and Afghanistan. Despite the fact that Assange is a famous and deeply polarizing figure, the real and full story of Assange, his imprisonment, how we came to be in prison, and why is rarely told, is a complex story and one that unfolds over almost 13 years now. So we decided to devote tonight's episode to telling and documenting that story, in part because of its 4th anniversary, in part because there is now growing momentum to secure his release, and in part because of how he has been treated and maligned and abused sheds significant light on the leaker whom The New York Times and Washington Post this week helped the FBI capture and arrest 21-year-old Massachusetts National Guardsman Jack Teixeira, who's accused of disclosing a wide range of classified documents that shed considerable light on the reality of what the United States is doing in the war in Ukraine.
There are obvious, important differences between the two cases, but what they both have in common is that unlike what appears almost daily in mainstream corporate outlets, namely, the CIA and the FBI giving authorized, propagandized leaks to those media outlets, they are both responsible for highly illuminating but unauthorized leaks of secret information, meaning information that embarrasses the U.S. Security State while informing the American people about their lies, deceit and corrupt conduct. Understanding what happened in Assange's case is very important in itself, but it also has added significance considering this week's event. And we will go through and put them in to connect the dots and tell you exactly what it is that has happened in the Assange case and what is now happening with the latest developments.
As a reminder, System Update, each episode of it, is available in podcast form on Spotify, Apple and every other major podcasting platform. Simply follow us on those platforms and you can rate and review us to help spread the word or follow and listen to us there.
For now, welcome to a new episode of System Update starting right now.
Julian Assange has spent four full years in a high-security prison in the United Kingdom called Belmarsh, which, in 2004, the BBC dubbed proudly the British Guantanamo Bay. It is a prison known for being notoriously harsh. It houses the worst violent criminals as well as terror suspects. Assange, for no good reason whatsoever, has been kept in that prison for four straight years, even though the only crime he has ever been convicted of is a misdemeanor bail-jumping charge stemming from his seeking asylum from Ecuador, back in 2012. And yet it was on April 12, 2019, so four years ago, and two days to this day, that Assange was arrested by British law enforcement agents who went into the Ecuadorian embassy and dragged him out there and brought him to Belmarsh Prison, where he has been held ever since.
The humanitarian aspect of this story is well known. He married his longtime girlfriend while in prison and had two young children with her – whom he has not been able to raise with her. And doctors, both for his mental health and his physical health, have warned that his health has been gravely degraded over the past four years, and there is a good likelihood that if he continues to be in prison, he will break and possibly even die. Prior to the four years that Assange spent in this British prison, he has been detained for seven years before that, going all the way back to 2012 when he sought asylum from Ecuador and went to the Ecuadorian embassy where he was granted asylum because Sweden was trying to force him to travel to that country where two women had claimed that he had sexually assaulted them, two women whom he had dated for several months who never made those allegations and then suddenly united and both claimed that he had been sexually assaulted. Sweden was seeking his extradition back to Sweden and he was willing to go, except for the concern that Sweden would turn him over to the United States. As we're about to show you had Sweden simply agreed, as both Ecuador and Assange's lawyers requested not to use his presence on Swedish soil as a pretext to then turn him over to the United States to stand trial for national security crimes, had Sweden simply agreed, If you come to Sweden and face these charges, we will not use your presence here to turn you over to the U.S., Assange would have gotten on the next plane to Sweden to face those charges. It was when the Swedish government refused to give those assurances that the Ecuadorian stepped in and said he was clearly in danger in terms of his political rights and his human rights from being turned over to the United States and sent to prison for the rest of his life for the crime of having reported on the United States government.
There's, I think, a very good strong case to make that Julian Assange is definitely one of the most consequential and intrepid journalists of the last, say, 50 years, if not the single most important pioneering journalist of his generation. He has almost certainly broken more major stories than almost every single employee of the mainstream media outlet combined. They don't hate Julian Assange, despite the fact that he's broken so many stories. They hate him precisely because of that – in part because he shined. He holds up a mirror showing what they really are. He is what they pretend to be. While the mainstream media constantly publishes stories that they dress up as leaks but in fact are nothing more than propaganda messaging tasks given to them by the CIA and the FBI and Homeland Security, which pick up the phone and pick their favorite reporter and tell them what to go plant in the newspaper to disseminate propaganda to the American people, Assange never does that and never had to and never would. He shows the American people and the world the secrets the CIA and the FBI and the Pentagon and Homeland Security don't want you to see. And that's why those agencies hate him. And that's why the employees and the media outlets that serve those agencies also hate him. That is the reason that he's in prison. Almost every single employee of The New York Times, The Washington Post, CNN and NBC, on a daily basis – you can pick up those newspapers or if you have the misfortune to listen to those networks, you will hear or read them saying – “anonymous officials told us” X, Y, and Z, they publish classified information all the time. But they don't end up like Julian Assange or Jack Teixeira – the 21-year-old member of the Massachusetts National Guard was hunted this week by The New York Times and The Washington Post and then arrested yesterday by the FBI because he is accused of having leaked classified documents. The difference between the mainstream media on the one hand and Assange and Jack Teixeira and people like Edward Snowden on the other is that the mainstream media publishes leaks that are authorized, that the U.S. Security State wants you to see because they're forms of propaganda and that's why they're never punished. That's why they don't end up in prison. They get book deals; they get put on television and they're applauded by the U.S. government. The people who end up in prison are those who show you the secrets they want to hide. That's the main difference. It's the difference between being a propagandist and being a journalist. Julian Assange is a journalist, and that's the reason he's in prison.
One of the things that struck me this week about this new leaker, this 21-year-old, is that it follows the same pattern that is always used whenever we have an unauthorized leak, meaning a leak the U.S. Security State did not plant themselves. You can go down and look at how Edward Snowden was treated, how Julian Assange is being treated, and even how Daniel Ellsberg was treated, or Chelsea Manning – you see exactly the same pattern in the way their media servants behave. So, one of the things that are being done, arguably the leading tactic that's being used to malign and demean this newest leaker is to try to do everything possible to distract your attention away from the substance of the documents that he allegedly enabled us to see. And while some documents made their way onto the Internet that I myself would not have published because they don't seem to be in the public interest, many of them are clearly in the public interest. We devoted our show on Monday and again last night to examining some of those documents, including the fact that Joe Biden ordered American Special Forces to be deployed on the ground to Ukraine. So, whether you're in favor of this war in Ukraine or not, whether you're in favor of the U.S. proxy war in Ukraine or not, the government and the media have hidden from you the rather important fact that the United States actually has troops or Special Forces on the ground participating in a hot war with Russia.
Those documents revealed that the United States and Zelenskyy both believe and have the position that there will be no negotiating, let alone a diplomatic resolution into 2023, which means they expect and want the war to extend at least through 2024. That's tens of billions if not hundreds of billions of dollars or more that you're going to be told you have to send to Kyiv and to Zelenskyy. Of course, that's something we ought to know. Some documents say that, as a result of spying on Zelenskyy, the U.S. government knows that he intends to use the weapons he's obtained from NATO and from the U.S. to strike deep into Russian territory, even though we were told repeatedly that the U.S. weapons would never be used to strike Russian territory, only to defend Ukraine, given the very serious risk that can spiral into escalation. And if you want to see all the other things these documents revealed, in the public interest, that we, as Americans, ought to know, because they revealed things that our government is doing in secret or reveal lies that they told about what they're doing. you can watch our show on Monday, you can watch our show last night or you can – for those of you who are Locals subscribers to our local community – look at the article we published. It's actually available. We made it available to everyone. It's not behind any paywall, so anyone can look at it where we've been compiling the documents that were leaked that we ourselves are reporting on. We want you to be able to see those documents that we don't believe that we get to see them and you don't. CNN, when they showed these documents, they blurred them. The New York Times and The Washington Post will talk about them but won't show them. We believe you have every right to see what your government is doing in the dark. And the reason we got to see these is that this 21-year-old decided that they should be seen.
But instead of focusing on these critically important revelations, there's instead an attempt to focus on his personality, to distract your attention away from the substance of the revelations, and instead get you to hate him or dislike him or think poorly of him so that you have a negative view of the things that he revealed and sad that your focus is on him as a person and not on the revelations themselves. So here, for example, is a Fortune Magazine article. There are countless of these doing the same thing. There you see the headline: “Alleged Pentagon leaker was a conspiracy theorist who shared racist memes and anti-Semitic ideas.”
I suppose that is relevant if you are trying to decide whether you like Jack Teixeira or not – I personally have a hard time believing it's uncommon that teenage forums, which is what this was, it was mostly 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21-year-olds. He was the oldest one. I have a hard time believing it's uncommon that people in these kinds of underground gaming communities don't say transgressive things. Oftentimes, teenagers or young adults in their early twenties say things not out of malice, but out of transgression. But be that as it may, assume, if you want, that he's racist and anti-Semitic, what does that have to do at all with the revelations that he enabled us to see? Nothing. As a journalist, I'm not interested in whether he's a pure person or a nice person with good political views. It doesn't interest me at all. Why would it? What interests me are the documents, and yet what the media is doing over and over and over is trying to get you to focus on his personality traits. This is exactly the same thing that was done when we first did the reporting in 2013, based on the documents provided by Edward Snowden that revealed the American government was spying on the American people en masse in violation of the Constitution and the law – it was unconstitutional and legal infringement of millions of Americans privacy rights and a court ultimately ruled that the program we revealed, the NSA indiscriminate domestic spying program, violated the Fourth Amendment and violated the law. And yet, instantly – we waited about a week, we did stories for a week. And then at Snowden's insistence, we put him on camera. We interviewed him so that he could step forward and say, You don't have to find me, I'm not hiding, I don't believe I did anything wrong. I believe I owe it to the American people to explain why I've done this. And he went on camera and said, “I began thinking the same things most people are taught to believe about the U.S. government.” He tried to enlist in the Army to fight in the Iraq war, but along the way, he became disillusioned when he saw that our government frequently lies to the American people. He explained that he saw that these systems were not being used against foreign threats like al-Qaida or ISIS but, instead, had been turned on the American people indiscriminately. And then he explained the final straw was when he heard James Clapper, the senior national security adviser for the Obama administration, went before the United States Senate and then falsely deny that the NSA was spying en masse on millions of American citizens. He had the evidence on his hand proving that James Clapper lied. The government was doing exactly that, which he falsely said it wasn't. And so, he came to myself and Laura Poitras and handed us this full archive of documents so that we could do the reporting and yet, soon as we unveiled them – and we knew this was going to happen – the focus immediately switched to away from what the NSA was doing to “Oh, Edward Snowden is a narcissist, he thinks he has the right to decide what should and shouldn't be revealed” – digging into his past blog posts in order again to get you to distract your attention away from what the substantive revelations were on to Edward Snowden as a person.
I think people have forgotten how aggressively that strategy invoked with Julian Assange was to create a climate in which Americans would come to regard him as someone who is untoward, somebody who provoked feelings of discomfort, all in order to personalize the leaks onto Assange and therefore not want to pay attention to the leaks.
Just to show you how far this went, here's an article that was published in 2011, just a few months after WikiLeaks concluded its first real major scoop, the one for which Assange is now being prosecuted, showing war crimes in Iraq and Afghanistan and the diplomatic cables that revealed U.S. allies around the world are deeply corrupt, in the Arab world and elsewhere. We'll show you exactly what WikiLeaks revealed in 2010, and how important those revelations were, but here is what the editor in chief, the executive editor of The New York Times of the time, Bill Keller, did just months after WikiLeaks. And remember, The New York Times participated in some of this reporting. They worked with Assange. Look at this paragraph that Bill Keller published, which he claims he got from one of his reporters right after he had met with Assange.
He [meaning Assange] was alert but disheveled, like a bag lady walking in off the street wearing a dingy, light-colored sport coat and cargo pants, dirty white shirt, beat-up sneakers and filthy white socks that collapsed around his ankles. He smelled as if he hadn't bathed in days (The New York Times. January 26, 2011).
Do you see that attempt to get you to think Julian Assange is such a dirty person in every sense of the word that you should forget about everything that WikiLeaks just revealed about what your government did, all the lies that it told you, just like they're doing with Jack Teixeira now?
Here's another similar headline published in Vox, in 2019, on the day that Julian Assange was arrested. This is Vox, a website filled with writers who have never broken a major story of any kind, let alone one that requires courage or that consists of standing up to powerful institutions. They should revere Julian Assange but, instead, they're shame bound. They think about him because he shows what they really are. And so, this is the kind of headline that they published on the day Assange was arrested in order to get you to focus on Assange, the person “Why Ecuador Released Julian Assange: Rudeness, Spying and Poop. He was the worst houseguest. Seriously, the worst.” I mean, that is really what they said. It's not just what they said, but the tone. It's like an adolescent. “He was seriously the worst houseguest.” Seriously, the worst. This is Alex Ward. I've never heard of this person. I know for a fact, by the fact that he works for Vox, that he's never broken a significant story. And yet he's utilizing the tactic that the establishment uses against anyone who brings incriminating and illuminating evidence to light about what the U.S. Security State does. And that is exactly what they did all the time with Assange.
I think it's worth recalling how WikiLeaks came into public prominence even before that 2010 major series of stories that they did about Iraq and Afghanistan because I think this has been somewhat forgotten. I remember very well the first day that I ever heard of Julian Assange. When I saw this article in The New York Times, on March 17, 2010, I was a journalist for Salon, and it is the first time I had really focused on WikiLeaks. I believe I had heard of them before because they had done some minor leaks, but this is the time I really focused on them. So, this is an article entitled “Pentagon Sees a Threat from Online Muckrakers,” and it's an article describing how the U.S. Army had prepared a report declaring WikiLeaks to be an enemy of the state and parting ways to destroy them. Here's what the New York Times reported,
To the list of the enemies threatening the security of the United States, the Pentagon has added WikiLeaks.org, a tiny online source of information and documents that governments and corporations around the world would prefer to keep secret. The Pentagon assessed the danger WikiLeaks.org posed to the Army in a report marked “unauthorized disclosure subject to criminal sanctions.” It concluded that WikiLeaks.org represents a potential force protection, counterintelligence, OPSEC and INFOSEC threat to the U.S. Army – or, in plain English, a threat to Army operations and information.
WikiLeaks, true to its mission to publish materials that expose secrets of all kinds, published the 2008 Pentagon report about itself on Monday (The New York Times. March 17, 2010).
So, in other words, the U.S. Army published a secret report declaring WikiLeaks an enemy of the state and plotting ways to destroy it, including by submitting fabricated or fake documents to WikiLeaks in the hope that they would publish it and destroy their credibility. WikiLeaks got a hold of that U.S. Army report and published it on their website. And then the New York Times did this write-up.
The New York Times went on:
WikiLeaks, a nonprofit organization, has rankled governments and companies around the world with its publication of materials intended to be kept secret. For instance, the Army's report says that in 2008, access to the website in the United States was cut off by a court order after Bank Julius Baer, a Swiss financial institution, sued it [WikiLeaks] for publishing documents implicating Baer in money laundering, grand larceny and tax evasion. Access was restored after two weeks when the bank dropped this case.
Governments, including those of North Korea and Thailand, also have tried to prevent access to the [WikiLeaks] site and complained about its release of materials critical of their governments and policies.
The Army's interest in WikiLeaks appears to have been spurred by, among other things, its publication and analysis of classified and unclassified army documents containing information about military equipment, units, operations and “nearly the entire order of battle” for American forces in Iraq and Afghanistan in April 2007 (The New York Times. March 17, 2010).
So, before WikiLeaks did its major story, the one based on the archive provided by Chelsea Manning, it did go around the world exposing corporate corruption, toxic waste dumping in Kenya, money laundering in a Swiss bank – and a Swiss banker actually sued WikiLeaks and got their website shut down for two weeks – as well as other acts that the United States government was doing in both Iraq and Afghanistan, to the point where even before those major leaks became before WikiLeaks came on the radar of everybody, the Army had declared them to be an enemy of the state and parted ways to destroy their reputation.
One of the things that WikiLeaks did, after all of that was, in 2010, they did get this archive from Chelsea Manning. That was the thing that put them on the map that made the entire U.S. Security State devoted to their destruction. Here is, for example, an article that I wrote after The New York Times published that article about the U.S. Army report when the U.S. Army was already planning to destroy WikiLeaks. And I wrote about it just based on that called Julian Assange, the day I saw that New York Times article, I interviewed him for Salon because I knew that the model he had created all the way back then was going to be pioneering in journalism. The model that he created was designed to allow sources around the world to furnish large amounts of digital information that institutions of power wanted to keep secret. This was the genius of Julian Assange. This is why he became so dangerous. Julian Assange realized before anyone else did that the future of journalism in the digital age was going to be large-scale digital leaks. And to facilitate that, he needed to provide a way for sources – people inside these institutions – to provide these leaks securely and safely. And so, what he did, using his skills as a computer programmer, was create a submission program that guaranteed anonymity to those providing this information. That's what made him so threatening. When Daniel Ellsberg published the Pentagon Papers in 1971, which were tens of thousands of top-secret documents that showed that the United States government was systematically lying to the American people about the war in Vietnam, one of the main problems Ellsberg faced back in 1971 was a logistical problem. If you want to leak tens of thousands of pages to a newspaper, how do you even copy it? Do you go to the local drugstore and carry a huge suitcase of dimes and just one after the next at the Xerox machine in the pharmacy copy page after page after page after page? That is similar to what Ellsberg ended up doing. But in the digital age, everything changed. It became extremely easy for someone inside an institution like Edward Snowden or Chelsea Manning or Jack Teixeira to take information very quickly by downloading it and then sending it to a journalist to publish it, curate it, to report on it. And Assange’s genius, his pioneering prescient anticipation and recognition was that all that you need to do was to create a safe way for sources to do that, and they would come to you. And that's what he created. He was able to hold all kinds of corporate and state institutions accountable before that big leak even happened. And that's what caused me to interview him and write about him in 2010 and the headline that I used at Salon, my first write about WikiLeaks – the first time – was “The War on WikiLeaks and Why it Matters.” The subheading was “The U.S. government escalates its campaign to harass and destroy a key whistleblowing site.” So, this war between Assange and the U.S. government has been long in the making, well before people even had heard of WikiLeaks.
The first leak that I ever wrote about back then is a really fascinating one. It's been lost to memory and it's been lost to history. This was, again, before the Collateral Murder video and all the things that he ended up showing. It was a CIA red cell letter. That was in March 2010. And a CIA red cell letter is a way that the CIA recognizes a certain problem in the world that's emerging and thinks about how they can try and solve it. The problem that this CIA red cell letter was anticipating and discussing, and it's one that WikiLeaks obtained and leaked – it’s fascinating. They were very worried that the war in Afghanistan was becoming increasingly unpopular. Listen to this! People in Western Europe started to wonder, why are we fighting a war in Afghanistan for nine years now? Why are we sending our sons and daughters to go fight and die in Afghanistan against the Taliban? How does this make any sense? Why are we spending billions of dollars on a war in Afghanistan when our standard of living is plummeting at home? And there had been two governments, one in the Netherlands and another one that had fallen in parliamentary elections, largely due to the popular anger that those governments wanted to keep fighting in the war in Afghanistan. The CIA was petrified that if anti-war sentiment about the war in Afghanistan continued to spread throughout Western Europe, every government that was fought over the war would lose or they would be forced to pull troops out. In other words, they would be forced to adhere to the wishes of the population. And you can't have that. So, this CIA red letter was to say, how are we going to fix this problem? And here you see this fascinating title of the CIA memo – and again, the only reason we know about this is because WikiLeaks published it – where they say, “Afghanistan: Sustaining Western European Support for the NATO-Led Mission – Why Counting on Apathy Might Not Be Enough.” That's an incredibly revealing phrase. The CIA knows that nobody was waking up in Western Europe or the United States in 2010 and wanting the government to send people to die and spend resources on the war in Afghanistan. What they count on instead is apathy. They go and they fight their wars in Syria and Libya and Iraq and Afghanistan and Ukraine, and they know it doesn't improve your life, they know that that's not what you want, but what they count on is your apathy. Then at some point, you just kind of give up. You say, “I can't do anything about it.” This war is going to go on for as long as they want it to, and there's not much I can do. It's apathy. And the CIA saying we usually count on apathy. That's how we get our way. That's how we're able to do things against the will of the population. But in this case, apathy may not be enough because anti-war sentiment is spreading throughout Western Europe. And so, their solution was to make Barack Obama the face of the war in Afghanistan because they knew that Western Europeans adored Barack Obama. They saw that Barack Obama was a tool of theirs, a marketing tool to take this war that was started by George Bush, whom Western Europeans looked at with disapproval. Bush was a swaggering American, an evangelical, religious Christian, something not popular in Western Europe and they replaced that face with the much more cosmopolitan and progressive face of Barack Obama. The CIA knew that if they could make Barack Obama the face of that war and give it a progressive rationale, they would stem the tide of antiwar sentiment in Western Europe and enable that war to continue. And that's exactly what happened. So here in this memo, the CIA says, “Appeals by President Obama and Afghan Women May Gain Traction.” That's the headline of what the CIA is saying: they knew that appeals by President Obama and using Afghan women would make Western Europeans agree to have this war continue,
The confidence of the French and German publics in President Obama's ability to handle foreign affairs in general and Afghanistan in particular suggest that they would be receptive to his direct affirmation of the importance to the ISAF mission – and sensitive to direct expressions of disappointment in allies who do not help (CIA Red Letter).
Isn't that fascinating? The CIA knew that Obama was a marketing tool for their wars, and that's what he became. And that worked. Western Europe stayed with the United States until the United States left Afghanistan.
That is the kind of thing that WikiLeaks is publishing. And that's why the U.S. Security State decided they had to destroy Julian Assange with things like having Bill Keller go and say his socks were filthy, he didn't take a bath. But then the big leak was the one that Chelsea Manning enabled, in 2010, that no matter what your views on those wars were, in Afghanistan and Iraq, in the War on Terror, unquestionably, we ought to have seen these things that WikiLeaks enabled us to see. This is the reporting in 2010, not what Julian Assange did in 2016 in the election, but this reporting is what he's being prosecuted for.
So, I could spend all night showing you what that reporting revealed but just to give you a couple of samples, here, from November 2010, there are documents that Hillary “Clinton ordered American diplomats to spy on UN officials.” (FP. Nov 29, 2010). Do you think Hillary Clinton, who at the time was the secretary of state, was appreciative that she got caught spying on UN officials? Here from The Guardian, you see “Iraq War Logs: Secret Order That Let U.S. To Ignore Abuse.” There was an order in place where the United States government knew that Iraqi security forces, which we were arming and training, were using torture and murder against dissidents to the regime we installed and there was an order in place telling American troops they were to ignore that and overlook it and not do anything about it. And then, of course, there was the most famous part of all, which was the video that WikiLeaks published showing American troops gunning down 12 innocent people, including two Reuters journalists, killing them all as they tried to crawl away and then shooting on the people who came in to rescue them, ambulance workers and the like as well. Let's take just a look at just a small portion of that video to remind you how Julian Assange became an enemy of the state to the point where he's in prison 13 years later.
Now, I don't think people are particularly surprised that wars entail the killing of innocent civilians, even sometimes what seemed to be deliberate, and you hear the troops kind of celebrating it. But images are very powerful and we should know what our government is doing in our name. We constantly see the victims in Ukraine so our emotions are whipped up to hate Russia and to be disgusted by the Russian war. But all the reporting that WikiLeaks did in 2010 as part of that reporting on Hillary Clinton, on the Clinton State Department in the Obama administration, what we were doing in Iraq and Afghanistan, what our allies around the world were doing, were all incredibly newsworthy. As I said, they were more significant and huge scoops than the work of almost every employee of media outlets combined. And it was at that point that our government decided that Julian Assange and WikiLeaks had to be destroyed at any cost – because he was too dangerous. And the reason he was too dangerous is that unlike the people who are working in the New York Times and The Washington Post and NBC and CNN, who do the U.S. Security State's bidding, who are little more than glorified messengers for the U.S. Security State, Julian Assange was doing real journalism and that is what we can't have. You can have all the guarantees in the Constitution that you want about a free press, but it's just words on parchment paper if we allow the government to then go and imprison those who do real reporting – and it's always with the aid of media outlets to destroy his reputation with the kind of stuff that I showed you.
That is basically part one, the first half, of what really happened to Julian Assange. That is what led to the determination of the United States government to destroy him. I think that part of the story is extremely significant. We're going to show you part two, which is what led to Assange's arrest and how that was effectuated, the reason why it's so morally grotesque and the most recent events that are giving some hope that he could be released.
But before we get to that, we have a new part of our show, which I'm about to explain in this clip I'm about to show you ways that, as an independent journalist and independent media, which is what we hear on this show are, we are now going to look for different ways that we can support our journalism. So, we just prepared a very quick video explaining how we're going to do that. And we will be back in just a couple of minutes. I hope you watch what it is that we taped.
Sponsored Ad:
As most of you know, this show System Update is independent journalism. We are part of independent media and what that means is we have no corporate management, no corporate structure to which we report that supervises or controls our show in any way. Being independent media, we need ways to fund the show to ensure that we can present to you a professional show here, in a professional studio, with a fairly large team that helps me and works with me to put the show together. And that in turn means that there are two ways we can do that. One is we rely on the viewer and reader support, which used to mean Substack subscriptions, and now it means people who join our community in Locals, and the other means we have sponsors for our show. That's something we decided to do when we launched it. That's a big necessity to do that. But what I made clear to everybody when that was proposed is that I would never, ever look into the camera and talk about a product that didn't completely align with my values and that I didn't feel my full integrity in order to talk about. And we have already rejected a whole variety of proposed sponsors, things like my recommending to you investment vehicles or different places to put your money or different companies that I didn't know much about and don't feel comfortable recommending because the trust that I've built up over the years with my viewers and my readers is something that is invaluable and I would never trade away. So, we are really excited to have our first sponsor, which is Field of Greens, that completely aligns with everything I believe in with my life, the way in which I live my life. And I feel not just willing but excited to recommend it. There are obviously a ton of supplements on the market. You probably hear about them all the time when you watch these shows, but this is a fruit and vegetable supplement that's specifically designed with each fruit and vegetable to target a specific part of your body, like your cardiovascular system, your liver and kidney health, your immune system, your metabolism. And some of you might know I am a vegan. I stopped eating factory food and meat many years ago. And in part it's because I love animals so much and didn't want to support their industrialized torture. But also, it's just for health reasons because factory farming food is just a vector of infection and disease and it's incredibly unhealthy. And as you start to get older, if you haven't already, you will start to see you have to start focusing on your health if you want to stay fit and energized. Field of Greens really helps you do that, it will immediately start making you feel healthier and more energetic. Your skin will be visibly brightened, your hair will look healthier, and you will be slimmer. And they really believe in their products so much that if you begin taking them and don't immediately see benefits, they actually give you a refund. They're very confident. I've seen that people who begin taking it, people start saying, you look young, what are you doing with your hair? Have you done something with your skin? It's just an overall fitness level that it really does provide you.
And so, as part of becoming our first sponsor, what they have done is they've created a way to help you get started, which is that you can get 15% off of your first order and another 10% off when you subscribe for recurring orders.
You just visit Fieldofgreens.com and use the promo code: Glenn.
That will help you and your health, it helps the show, and it enables us to have sponsors that are only the kinds of sponsors that I feel very good about having and that are in full alignment with my values and the way I live.
So, when we left off, we had just explained the huge bombshell that was WikiLeaks’ reporting, certainly even before the major scoops of 2010 but then, through 2010, I don't think it's difficult to understand why the government and its servants in the media were so enraged with what WikiLeaks and Julian Assange had done.
The problem became how was it? How could the government possibly destroy WikiLeaks and Assange for reporting – even the United States under Obama? It was a bridge too far to be explicit about the fact that they wanted to go and arrest somebody and put them in prison for the reporting that they just did of the kind that I just showed you. So, lo and behold, in 2010, that was when there appeared to materialize two women who claimed that Assange had sexually assaulted them, that they began having sex with him consensually and at some point, requested he uses a condom. He didn't use a condom and, under Swedish law, that's considered sexual assault or even rape. And Assange was more than willing to go to Sweden to face those charges as long as Sweden agreed not to use his presence on their soil as an excuse to turn them over to the United States – as Sweden, as a close American ally, had done in the past. When Sweden refused, that was when he sought asylum in the embassy.
The so-called rape investigation in Sweden was dropped in 2019. They couldn't get the evidence that they needed to do that. They claimed it was because he had waited long enough but the reality was, he was more than willing to be interviewed in the Ecuadorian embassy. The Swedish investigators kept saying they couldn't do that because they wanted to lure him to Sweden. It was so obvious what they were doing. They wanted to get him to Sweden to give him to the U.S., whereas the British had a slightly more independent court system. And then when they couldn't, they finally went and interviewed him and then they dropped the case. So, there's no more sexual assault or rape investigation. That has been closed. He was never charged with that, let alone convicted of that, so, that has nothing to do with why he's now in prison.
When they went in to arrest him, they charged him with bail-jumping, meaning, back in 2012, he was scheduled for a court date and instead of going to court, he got asylum from Ecuador. Every sovereign state grants asylum. The United States grants asylum all the time to people who are wanted back home for crimes. It's a recognized right. He was convicted of bail jumping. He got the maximum 50-week sentence and he's long ago served that. He served that from 2019 to 2020. So, there are no more pending charges against him in the UK. He is not serving any kind of sentence for jail time. The only reason he's in prison is that the Biden administration is pursuing this in this indictment and demanding he is extradited to the United States – and pending that extradition, the British refused to let him out of prison. They're basically holding him on without bond.
Even though, as I said before, even under Obama – who prosecuted more whistleblowers than all previous presidents combined under the Espionage Act, he was incredibly aggressive when it came to prosecuting journalists and their sources – even under the Obama administration, as they said, they couldn't prosecute Assange for doing reporting. But they did try. They convened a grand jury. They investigated WikiLeaks for two or three years. They made clear they wanted to find a way to prosecute him. They wanted to prove that he conspired with Chelsea Manning to get those documents, that he didn't just passively receive them, but they couldn't find any evidence. And so, in 2013, there you see from The Washington Post, the Obama administration acknowledged that they were unlikely to prosecute Julian Assange. The article reads,
Julian Assange Unlikely to Face U.S. Charges Over Publishing Classified Documents.
The Justice Department has all but concluded it will not bring charges against WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange for publishing classified documents because government lawyers said they could not do so without also prosecuting U.S. news organizations and journalists. According to U.S. officials.
The Obama administration has charged government employees and contractors who leak classified information – such as former NSA contractor Edward Snowden and former Army intelligence analyst Bradley Manning – with violations of the Espionage Act. But officials said that although Assange published classified documents, he did not leak them –something they said significantly affects their legal analysis. (The Washington Post. Nov. 25, 2013).
In other words, he published them but did not leak them.
The problem the department has always had investigating Julian Assange is there is no way to prosecute him for publishing information without the same theory being applied to journalists,” said former Justice Department spokesman Matthew Miller. And if you're not going to prosecute journalists for publishing classified information, which the department is not, then there is no way to prosecute Assange (The Washington Post. Nov. 25, 2013).
That is a really important point there, which is that it wasn't just Julian Assange that published those documents from the Iraq and Afghanistan war logs and the diplomatic cables. News outlets like the New York Times and The Guardian also published them. And so, the question was, how can you possibly prosecute Julian Assange but not prosecute the media outlets that publish the same documents? The Obama Justice Department, though, they tried, concluded there was no way to do it. But the pressure continued to build because the establishment was adamant that Julian Assange be convicted.
Here you see from The Economist, an editorial entitled “Why Julian Assange Should be Extradited? The WikiLeaks co-founder is accused of hacking, not leaking, and that is a serious crime,” says The Economist, in 2019.
Dianne Feinstein, the Democratic senator from California, published an article, an op-ed in The Wall Street Journal in 2010 urging, “Prosecute Assange under the Espionage Act.” The California Democrat wrote, “Just as the First Amendment is not a license to yell ‘Fire’ in a crowded theater, it is also not a license to jeopardize national security.” So, The Economist, Dianne Feinstein were demanding Assange be prosecuted, notwithstanding the difficulty of how you prosecute Assange for doing the same thing journalists do. And I'm sure most of you don't remember this – or maybe you never saw it – but back in 2010 or 2011, Joe Biden, the then-vice president under President Obama, went on “Meet the Press” and he called Julian Assange a “high tech terrorist.” Look at this video.
(Video. ABC News. July 12, 2007).
Meet the Press: Here is classified material. Mitch McConnell said he's a high-tech terrorist. Others say this is akin to the Pentagon Papers. Where do you come from?
President Biden: I would argue that it's closer to being in the high-tech terrorists than the Pentagon Papers.
Do you see what the media does? Julian Assange is doing their job and in turn, they turn around and are laying the foundation for the government to prosecute him for doing what they pretend to do. As a reminder, I went to “Meet the Press” shortly after I began publishing the Snowden materials. And there, that host, David Gregory, asked me twice whether I should be also imprisoned, along with Edward Snowden, for the work that I was doing. He then convened a panel with Chuck Todd and others, people, again, who have never broken a story of any kind and they all sat around talking about how I'm not a real journalist, how I probably could and should be prosecuted. The next day, Andrew Ross Sorkin of The New York Times went on a CNBC show and he urged that I be imprisoned alongside Snowden. He eventually apologized, but that is what these media outlets do. They are vicious agents for the U.S. Security State. They don't do journalism. They're propagandists for the U.S. Security State and they despise anybody who does real journalism like Julian Assange. So that was the climate at the time. You have establishment voices demanding Assange be prosecuted, even though the Obama Justice Department is saying, we want it, but we can't.
And so, he kind of just stayed in the Ecuadorian embassy from 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, and 2016 through the Obama administration. And what changed? And some of you may not want to hear this, but it is nonetheless true, the person most singularly responsible for the fact that Julian Assange ended up being indicted in 2019, not under the Obama administration or the Biden administration, but under the Trump administration, was Mike Pompeo, the person I regard as Donald Trump's biggest mistake? Several neocons exploited Trump's worst character flaw, which is that he's easily manipulated by anybody who flatters him. He was just on an interview with Tucker Carlson talking about how he refuses to criticize Gavin Newsom because Gavin Newsom, the California Democratic governor, says good things about Trump and said good things about Trump – if you say good things about Trump and flatter him, he will keep you in his good graces.
Mike Pompeo was very clever and very smart and knew how to do that and wiggled his way in to being Trump's CIA director first, he was the head of the CIA under Trump and then his State Department, his Secretary of State. Mike Pompeo, when he was at the CIA, gave a speech where he stood up and vowed to see at the CIA that he would do everything in his power to destroy WikiLeaks and ensure that Julian Assange would never be free again. I reported on that speech at the time. I was at The Intercept. There you see the headline in 2017. The headline is “Trump CIA Director Mike Pompeo Targeting Wikileaks Explicitly Threatens Speech and Press Freedoms. Why is the U.S. press corps so silent about an actual threat to press freedom?” This is when the media was whining every day about mean things Trump was saying about Jim Acosta or Wolf Blitzer or Chuck Todd. And what I was writing to say as I listened to that speech was that I had never heard a more direct assault on press freedom than Mike Pompeo at the CIA, the CIA director, vowing to do everything in his power to destroy Julian Assange. Here's the article.
In February, after Donald Trump tweeted that the U.S. media were the “enemy, the people,” the targets of his insult exploded with indignation, devoting wall-to-wall media coverage to what they depicted as a grave assault on press freedoms more befitting of a tyranny.
By stark and disturbing contrast, the media reaction yesterday was far more muted, even welcoming, when Trump's CIA director, Mike Pompeo, actually and explicitly vowed to target freedoms of speech and press, in a blistering, threatening speech he delivered to the DC think tank Center for Strategic and International Studies.
What made Pompeo's overt threats of repression so palatable to many was that they were not directed at CNN, The New York Times, or other beloved-in-DC outlets, but rather at WikiLeaks. [Pompeo] stood up in public and explicitly threatened to target free speech rights and press freedoms, and it was almost impossible to find even a single U.S. mainstream journalist expressing objections or alarm because the targets Pompeo chose in this instance are ones they dislike – much the way that many are willing to overlook or even sanction free speech repression if the targeted ideas or speakers are sufficiently unpopular.
Decreeing (with no evidence) that WikiLeaks is a “non-state hostile intelligence service often abetted by state actors like Russia,” a belief that has become gospel in establishment Democratic Party circles – Pompeo proclaimed that “We have to recognize that we can no longer allow Assange and his colleagues the latitude to use free speech values against us.” (G. Greenwald. April 14, 2017).
Pompeo: ‘We can no longer allow Assange and his colleagues the latitude to use free speech values against us.’
[Pompeo] also argued that while WikiLeaks “pretended that America's First Amendment freedoms shield them from justice,” but “they may have believed that, but they are wrong.”
He then issued this remarkable threat: “To give them the space to crush us with misappropriated secrets is a perversion of what our great Constitution stands for. It ends now.” At no point did Pompeo specify what steps the CIA had to take to ensure that the “space” to publish secrets “ends now.” (G. Greenwald. April 14, 2017).
So that was really the event that turned the tide against Julian Assange. He was still forced to stay in the Ecuadorian embassy, which certainly was not very good but it was Mike Pompeo who insisted that the Trump Justice Department devote itself to turning him into a felon and prosecuting him. And that's where the current criminal investigation of the Biden administration is now pursuing and demanding Assange be extradited to stand trial for it. That's where it began with Mike Pompeo and the CIA.
Here's The New York Times article that reported on how that happened. The headline is “How the Trump Administration Stepped Up Pursuit of Wikileaks’s Assange.” And there you see the article:
Soon after he took over as CIA director, Mike Pompeo privately told lawmakers about a new target for American spies: Julian Assange, the founder of WikiLeaks. Mr. Pompeo and former Attorney General Jeff Sessions unleashed an aggressive campaign against Mr. Assange, reversing an Obama-era view of WikiLeaks as a journalistic entity.
For more than a year, the nation's spies and investigators sought to learn about Mr. Assange and his ties to Russia, as senior administration officials claimed to believe he was in league with Moscow (The New York Times. April 13, 2023).
And then that is when the indictment came. It's in 2019. It's from the U.S. Attorney's office in eastern Virginia, and there's a press release: “WikiLeaks founder Charged in Computer Hacking Conspiracy.” (U.S. Attorney’s Office. April 11, 2019).
The problem with this case here is twofold. Number one, they're charging him under the Espionage Act of 1917. That is an archaic law that was implemented by Woodrow Wilson in order to criminalize Americans who dissented from Woodrow Wilson's desire to involve America in World War I in Europe. And the law is written to be impossible to defend yourself against. It makes it an absolute crime to publish classified information. This is the law that they're using to charge Edward Snowden with as well. And under this law, it is not a defense to say, yes, I publish classified information, but I was justified in doing so because the U.S. government was abusing the classification powers and secrecy powers to hide its crimes. When Edward Snowden sought asylum in Russia, people like Nancy Pelosi, John Kerry and Hillary Clinton kept saying, ‘Oh, if he's such a brave whistleblower, let him come back and convince a jury – they would’ never be able to say that now but, in 2016, they could say, let him man up and convince a jury that what he did was justified. It was a total lie. Under this law, you're prohibited from even raising that as a defense. That was Daniel Ellsberg's plan: to go into court and say, yes, I read the Pentagon Papers, but I was justified. And that was when the court ruled under the Espionage Act, you're not allowed to even raise that as a defense. It's almost impossible to win. The only reason Daniel Ellsberg is not in prison for the rest of his life is because the Nixon administration, the CIA, the FBI, broke into his psychoanalyst office. Remember earlier I was saying that the tactic used against whistleblowers is to focus you on their personal character, to distract attention from the revelations. So, when Daniel Ellsberg proved that the U.S. government was lying about the Vietnam War, knowing internally they couldn't win by telling the public they could win, their tactic was to go to his psychoanalyst office and break in and discover his psychosexual secrets. They got caught, and only for that reason did the court dismiss the criminal indictment against Daniel Ellsberg. That's the only reason he didn't go to prison for the rest of his life. This Espionage Act is written to make it impossible for anyone to defend themselves, and that's what they want to charge Julian Assange and Edward Snowden with. And secondly, they're doing it on purpose in eastern Virginia, which is notorious for having very pro-National Security State judges, and especially a community in which CIA agents and FBI agents and operatives of the U.S. Security State – this is where they all live. So, the jury is going to be composed of U.S. Security State operatives or people who support this Security State. Everything about this is making it impossible to win.
I think it's really important to note that while a huge amount of establishment support is in favor of Julian Assange being in prison – from the media, from the economist, from Dianne Feinstein, from Joe Biden – there's also a very significant and I would even say growing opposition, mostly people who are anti-establishment on either the left or the right. During the Trump era. one of the leading voices in the country crusading for a pardon for Julian Assange, which Donald Trump, by all reports, almost gave – and I was involved in those efforts to get a pardon for Snowden and Assange I know it's true that Trump did almost do it. I think one of the worst things Trump did was left office without giving either of them a pardon. I once did a video report explaining why that happened. The impeachment was hanging over his head, the second impeachment. Republicans like Mitch McConnell and Lindsey Graham and Marco Rubio said to him, if you pardon either of them or if you declassify CIA documents on your way out, we will vote to impeach you. I'm not excusing Trump, I'm just saying why he didn't do it. But there were a lot of people crusading for Assange. One of them was Tucker Carlson, the most-watched cable-news host in the country. He went on at least 20 or 25 times, both during Trump and since, and urged the public to support a pardon for Julian Assange, insisting that Assange, far from being a criminal, is actually a hero. Let's just look at one of the many times he did that.
(Video. Tucker Carlson Tonight. Sept. 20, 2021).
Tucker Carlson: Julian Assange has been in jail for an awfully long time. He's now in jail in the UK and was under house arrest in a foreign embassy in London. The U.S. is now accused Julian Assange of violating the Espionage Act. That's been going on for a long time and it's just dumb weird. It took us a very long time – years – to ask the obvious question: what exactly did Julian Assange do wrong? All good people hate Julian Assange. What was his crime exactly? Was he hacking into other people's computers or was he stealing secrets from the U.S. government? No, actually, he was publishing things. He was a journalist. He was an editor. That's literally true. Can you throw editors in jail because they embarrass you? Probably shouldn't. Not a good precedent to set. Even if you don't like the person's politics, you should be against that.
Here's to me the most repellent part of this entire monstrosity of keeping Julian Assange in a high-security prison for four years and trying to imprison him for life. Back in 2010, when the reporting was done, based on the archive about Iraq and Afghanistan, there was a lot of support among American liberals on the left for Julian Assange. Back then, when I was writing constantly in support of Assange when I was reporting on WikiLeaks, I was getting a lot of support from liberals and leftists and even mainstream Democrats who recognized in Assange the attributes of a journalist. A lot of them were against the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, and they were therefore happy that he had exposed the crimes being conducted by our government in the name of that war.
Now, though, it is almost impossible to find any liberal or leftist or Democrat to say anything positive about Julian Assange. And the only thing that changed from 2010 that made that true is that, in 2016, Julian Assange enabled reporting that was harmful to Hillary Clinton's candidacy because it shed incriminating light on how the Democratic National Committee was cheating on behalf of Hillary Clinton and against Bernie Sanders. You may recall that the top five officials of the Democratic National Committee in the middle of the 2016 campaign had to resign in the wake of the revelations that Julian Assange reported, including the party chairwoman, Debbie Wasserman Schultz. It was a major scandal for Democrats. And there were other incriminating documents about Hillary Clinton's secret speeches she gave to Goldman Sachs, where she was paid $500,000 or $750,000 that she refused to release, and she would go to Goldman Sachs and say, ‘I'm on your side,’ ‘You are the job creators.’ All the things that she would never say in public. There were all kinds of reports about corruption in the Clinton campaign and in the Democratic Party that Julian Assange disclosed as part of the 2016 election, doing the job of a reporter.
Nothing that he's being charged with, nothing that he's been indicted for is based on anything he did in the 2016 campaign. He's not charged with being a Russian agent or anything like that. But the reason Democrats are now so supportive of the attempt to prosecute – indict and prosecute him and extradite him – and the reason the Biden administration is so committed to putting him in prison is that he did reporting that was incriminating to the Democratic Party presidential candidate. That's why they want to put him in prison – because he reported truthful information that reflected poorly on Hillary Clinton. It is bad enough. It is completely despotic and tyrannical to want to put a reporter in prison for reporting on classified information, but it's infinitely worse to want to put them in prison because they did political reporting that undermined a Democratic Party politician. And that is the real reason they want to put him in prison. In that sense, he really is a political prisoner. On the surface, on the face of the indictment, he's been indicted for what he did in 2010. The reality, though, is they want to see him rot in jail because of what he did in 2016.
Just to give you an indication of how bad things were for Julian Assange, even before he went to prison, while he was in the Ecuadorian embassy, the CIA had hired contractors to spy on everything that he was doing inside the Ecuadorian embassy. Here is, for example, a 2019 article from the Spanish daily newspaper El País that is headlined: “Russia and U.S. Visitors Targets for the Spanish Firm that Spied on Julian Assange. The CIA had access to the server where the company stored the profiles of hundreds of people who visited the WikiLeaks founder during his stay in the Ecuadorian embassy in London.” The CIA was spying on everything Assange was doing in that embassy and on every one of his meetings.
In late 2017, I went to London as a journalist with my husband, David Miranda, who was a member of the Brazilian Congress and we visited Julian Assange. We spent several days with him in the embassy in London. And I read this El País article that indicated that I was one of the people on whom the CIA spied – so, my government was spying on me when I was, as a journalist, going to visit Julian Assange. This surveillance footage that the CIA contractor took of me and my husband, David Miranda, who, again, was a Brazilian congressman at the time, visiting Julian Assange, surfaced on the Internet. Let's take a look at that.
01:16:15
(Video. CIA Surveillance Footage of Ecuadorian Embassy)
When you talk about attacks on press freedom, an assault on a free press, this is what one means. Putting Julian Assange, forcing him into a tiny little room for seven years, where he sought asylum because he knew if he were forced to go to Sweden, they would turn him over to the U.S., and then the proof that he was right all along and that wasn't paranoia, is the fact that the U.S. is now trying to get their hands on him and he spent four years in a maximum security prison. With no end in sight. The Obama the Biden administration wants to ship him here in order to convict him of espionage charges that would probably send him to prison for decades, likely the rest of his life, given the very fragile state that he's in, he couldn't even go outside one time for all those seven years. Even prisoners get sunshine. When he was in the Ecuadorian embassy, it was basically a one-bedroom apartment. Inside. He was constantly being spied on. And he has had his freedom and his liberty deprived for more than a decade now because he believed it was important to hold the U.S. Security State and the U.S. government accountable.
What sickens me to my core is that the whiny propagandist in the corporate media during the Trump years constantly pretended that they were endangered because Trump would say mean things about them. Let's remember that Jim Acosta – that baloney-dried pedicure hack who has never broken a single story of any significance in his life, who tells his viewers, whatever the CIA and the FBI tell them to – wrote a bestselling book that liberals ate up called “The Enemy of the People - A Dangerous Time to Tell the Truth in America.” He depicted himself as some sort of martyr to press freedom because Trump would occasionally ridicule him, justifiably so, pointed out that CNN is an outlet of fake news, which they are, and occasionally tweeted about him. To these coddled people, that is persecution. Real persecution is what's happening to Julian Assange and what is about to happen now to this new leaker as well.
Let me just conclude by saying here that the reason this case matters so much is it goes far beyond Julian Assange. I think it is important to demand Assange's freedom because of the travesty of this case, that this father of two young children, this husband, this son, this brother is in prison, wasting away one of the most talented journalists of his generation because the U.S. government hates what he did. But the theory they're using to prosecute him is what is so dangerous. The argument that they're making is that Julian Assange didn't just passively receive information from Chelsea Manning, but he actively conspired with her to get it. Remember when the Obama administration wanted to prosecute Julian Assange, they knew that they had to prove that Assange actually conspired with Manning, that he somehow helped her get that information because if not, they were going to be criminalizing journalism itself. If all Assange did was get the information from Manning, he's like every other journalist. That's what I did in the Snowden case and what I did in the Brazil case. It's what the Pentagon Papers reporters did. You get information from a source and you publish it. And if you criminalize that, you're criminalizing journalism itself. So, the Obama administration knew they had to find something extra Assange did, and they looked everywhere and they couldn't find it and that was why they didn't prosecute him. What Mike Pompeo did was concocted a theory, along with the Justice Department, that what Assange did was he joined Chelsea Manning’s conspiracy for two reasons. Number one, he tried to help her evade detection by helping her get into the system using a different password. It didn't work. She had already given him the documents by the time he attempted that. And that is what journalists do all the time. Of course, you're supposed to help your source evade detection. If a source calls you on the phone, on an open phone line, and says, hey, let me tell you about government secrets that I've learned about, you're going to interject and say, no, don't do that. Don't use an open phone line to call me. Call me on some encrypted channel like a signal or something safer. If you go to The New York Times and The Washington Post. You will find a guide that they publish for their sources on how to communicate with them safely so they don't get caught.
If it is now a crime for a journalist to give instructions or information to a source on how not to get caught, investigative journalism itself will be criminalized. Every good journalist, by definition, does that. Journalists don't only have the right, but the obligation to help their sources avoid detection and getting caught, which is one of the things that is so repulsive about what The New York Times and The Washington Post did this week in helping the FBI find this leaker, even though it wasn't technically their source because he didn't give the documents to them – which is why they're so angry about it, he put it on Discord. – they did use the materials. They reported on materials. They recognized it as being newsworthy. And then, they turned around and helped the FBI find the source of this information that they implicitly recognized as newsworthy. Embedded in the journalistic ethos is that you protect sources, you regard as heroic the people who provide transparency to these powerful institutions. You don't try and work with the FBI to find them and hunt them down and deliver them to be arrested. It's completely unjournalistic to do that. And that's what makes the indictment of Assange so dangerous it is a theory that says if you advise your source on how not to get caught, you become a criminal.
The second theory they're using is that he never hacked into any government databases, he never himself stole information, instead, they say once Chelsea Manning gave him those documents, he encouraged her to go back and get more. I cannot put into words how common that is for every journalist to do. If a source comes to you and says, here is a bunch of information to enable you to break a huge story, of course, you're going to say to that person, wow, this is fantastic. Thank you for providing that. Are you able to get something showing X, showing Y, or showing Z as well? Every good journalist would do that. And just to illustrate how dangerous this precedent is that they're trying to set if they prosecute him, when the Brazilian government tried to prosecute me for the reporting I did here in Brazil, that proved that the top judges and prosecutors were corrupt, they actually brought charges against me and they copied the theory of the indictment that the U.S. is using against Assange by trying to say that there was a certain point I told my source, ‘you don't need to keep copies of our chat because if you do, that will enable you to get caught. Instead, I have copies of the chats and we will keep them all, so there's no reason for you to keep them all.’ They tried to convert that into my giving advice to my source as to how not to get caught and then, instead, I became part of the conspiracy when I did that. That's how dangerous that theory is.
In my case, the court stepped in and said, freedom of the press, and the Brazilian constitution protects me from being prosecuted for that. But unfortunately, in the U.S., the climate is such – a climate created by the media – that has produced so much contempt for Assange, primarily due to what he did in the 2016 election, but also all of these legal tools that have been developed over the years – the Obama administration using the Espionage Act 1917, over and over and over again, that it's almost impossible for anyone charged with these crimes to escape – and for all the talk about how Trump endangered press freedom by calling Wolf Blitzer stupid and by making fun of Jim Acosta. The real assault on press freedom, by far the gravest one that we face, is what is being done right now by the Biden administration to Julian Assange.
There are people on the right wing of the Republican Party, like Marjorie Taylor Greene and Matt Gaetz, who are agitating on behalf of Assange and urging that he be pardoned and the prosecution be dropped. Just this week, finally, there are a few members of the Squad and on the left wing of the Democratic Party, like Rashida Tlaib and Cori Bush and Jamaal Bowman, and even AOC, signed the letter who are urging that the prosecution be dropped as well. There's international pressure. A lot of world leaders believe that Julian Assange is a hero. All major press freedom groups in the West, including the ACLU, have banded together to urge that the prosecution be dropped.
The problem is that the media has done such a good job demonizing Julian Assange, just like they're now in the process of doing with this new leaker, that it's very, very difficult to argue that Julian Assange should be freed and that what he did is journalism. And that's primarily because the corporate media has inverted the idea of what journalism is. They do publish leaks of classified information all the time, but those are the leaks the CIA, the FBI and the Pentagon want you to see. Those are the leaks to propagandize and deceive you. You know that every day you read The New York Times, The Washington Post, and it says, “Intelligence officials tell us X, Y, and Z,” and they give them anonymity to make it seem like it's some edgy, unauthorized leak when in fact it's officially sanctioned leaks. That's what these journalists are. They’ve officially sanctioned tools of propaganda. The only people who are real journalists, or real transparency agents, you can recognize easily because those are the people the government tries to destroy, the media tries to destroy, including people like Julian Assange, who is now in prison.
And now there's a website that you can go to where you can lend your name to what I think is the vital cause to drop the prosecution of Julian Assange. It's called https://dontextraditeassange.com/. That is a website that has been constructed by the people who are coordinating his defense. I really encourage you to do so.
I'm not pretending here to be neutral. As a journalist, I think it is extraordinarily dangerous to create a precedent that allows the U.S. government to imprison Julian Assange. I'm in favor of transparency, not indiscriminate transparency. When I do journalism, like with the Snowden story or with the WikiLeaks story or the Brazil story, I don't just dump everything onto the Internet. I believe in curating it carefully so that the information that's published is what you need to see in order to know the truth about what your government is doing. But when there's reporting that exposes the lies that the government is telling you, especially about matters as fundamental as war or how your government is spying on you, the people who enable that are not criminals, they're heroes. And that most definitely includes Julian Assange.
So, on the fourth anniversary of his imprisonment in a high-security, maximum-security, prison in the UK for the crime of doing real journalism, something unrecognizable these days, given the dominance of media corporations, I want to do everything I can to illuminate the reality of what has happened, which is why we devoted the show to it tonight. It also sheds a lot of light on what's occurring with this new leaker as well. But I also really want to encourage you not just to listen to what I say in terms of the reporting, not just to be informed, not just to be angry, not just to be outraged, but to do everything that you can to agitate for his liberation as well. Because ultimately, journalism is about serving the citizenry. It's about ensuring that, you know what the most powerful institutions are doing, not the lies and the propaganda that they feed you using our nation's largest media corporations.
So that concludes our show for this evening because we did not do our live Locals show last night and we are out of time, we will be back next week with our live Locals show that follows this show on both Tuesday and Thursday, which we take your questions, respond to your feedback, and we'll listen to your suggestions about things we should cover or guess we should interview. Remember, we are available in podcast form. We encourage you to follow us there if you want to join our Locals community, which really helps our journalism and gives you access to the show’s transcripts that we publish every day after the show, as well as my journalism and other community figures. You can hit the red join button and become part of our Locals community. Thank you so much for making the show such a success. We hope to keep seeing you back here on Monday night and every night at 7 p.m. EST, exclusively here on Rumble.
Have a great weekend, everybody.